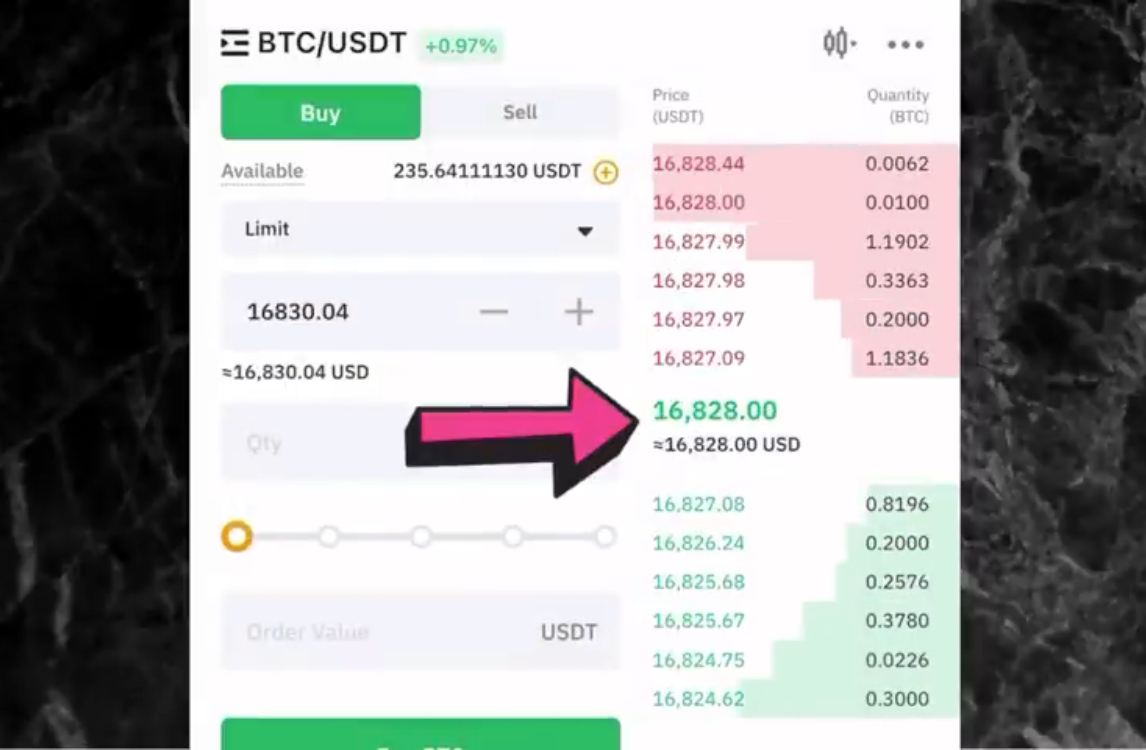
When trading cryptocurrencies, understanding the various order types is crucial for executing your strategies effectively and managing risk.
Some common order types in trading.
Market Order
Execution: Immediately buys or sells at the best available price in the market.
Pros: Fast and efficient for executing trades quickly.
Cons: Can result in slippage, especially during volatile market conditions.
Limit Order
Execution: Buys or sells only when the market price reaches a specified limit price.
Pros: Allows you to control the price at which you enter or exit a trade.
Cons: May not be executed if the market price doesn’t reach the limit price.
Stop Order
Execution: Becomes a market order when the market price reaches a specified stop price.
Pros: Helps protect against losses by automatically selling when the price drops below a certain level.
Cons: May be triggered prematurely during market fluctuations.
Stop-Limit Order
Execution: Becomes a limit order when the market price reaches a specified stop price.
Pros: Provides a degree of price control while protecting against losses.
Cons: May not be executed if the market price doesn’t reach the limit price after the stop price is triggered.
Trailing Stop Order
Execution: A stop order that adjusts its price based on the market price, creating a trailing stop that moves with the price.
Pros: Helps capture profits as the price moves in your favor.
Cons: May not be as effective in volatile markets.
Fill or Kill (FOK) Order
Execution: Requires the entire order to be filled immediately or canceled.
Pros: Ensures that the trade is executed at a specific price.
Cons: May be difficult to fill during low liquidity periods.
Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Order
Execution: Fills as much of the order as possible immediately and cancels the remaining portion.
Pros: Allows for partial fills.
Cons: May not fill the entire order if liquidity is low.
Watch Video to set some basic order time.